

Trail is the horizontal distance between the point where the steering. Negative values: hub follows the steering axis (fork "bent backward"). Learn all about Trails role in bike geometry in the Bike Insights Cyclopedia. The Dynamic Steering block implements dynamic steering to calculate the wheel angles for Ackerman, rack-and-pinion, and parallel. If wheels remained parallel, the kart would slides. Positive values: hub preceeds the steering axis (as shown in the image). While on a bend, the front wheels have different trajectories. Drag the car body up / down and left / right with the mouse to. The suspension travel analysis allows you to see what happens to the suspension during travel. Here defined as the angle between the floor behind the front wheel and the steering axis (see image above).ĭistance between the contact point (center of the contact patch) of the front wheel on the floor and the point where the "virtually" elongated steering axis meets the ground. Suspension calculations include coil and leaf springs, anti-roll bars, animated suspension geometry analysis with roll center and instant center (for dual A-arm and strut suspensions). This happens when wheels are further apart at top than at. Camber angle is positive when this is outward. Camber:- Camber angle is the angle between the vertical line and centre line of the tyre when viewed from the front of the vehicle.
#Steering geometry calculator download
TopOfPage | SteeringGeometr圜alculator | WheelDiameterTable | Text | Formulae There are five steering geometry angles : Camber Caster king pin inclination Toe in & Toe-out on turns. Clicking the links below will download (or attempt to open) the files. Trail passes zero (turns to negative values) if the steering is turned by
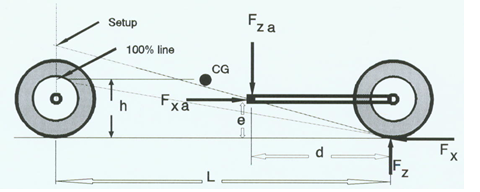
The comma as well as the point may be used as decimal point.įurther results from the above steering geometry data: Steering Kinematics - Geometric parameter calculations. The input field of the variable to be calculated must be empty. Your browser doesn't support JavaScript, or JavaScript has been disabled.

In 1818, Rudolf Ackerman patented a design of Georg Lankensperger that provided a steering system for carriages that eliminated the angle scrub and subsequent wear of the wheels on the front axle. Providing for required wheel turning angles in the steering linkage & wheel envelopes. You can watch the picture of the chassis move, and at the same time, the suspension. Turning circle, link lengths & inclinations Source: STEERING MECHANISMS Kinematics of Machines Tutorials Engineering Tutorials Here’s an illustrative calculation The Ackermann Principle as Applied to Steering (Automobile) 2. The chassis outline (blue lines) can be dragged up and down and rolled from side to side with the mouse (or moved with the scroll bars). (inches along x-axis) Frame bottom to lower mount Y. Ride height (Frame bottom above ground) (inches) Frame center to lower mount X. The roll center is affected by many different changes to the suspension, including camber link length, camber link ball stud locations, arm length, pin height, axle height, and others.Geometrical Relation between Head Tube Angle, Trail and Fork Offset In order to do this I will start with a description of Ackerman steering which forms the basis for Anti-Ackermann steering. Steering geometry / simulation including Ackermann steering Torsion bar rate - solid or tubular bars A-arm simulation. Double wishbone Macpherson strut Swing axle Sliding pillar Trailing arm. If you lower the car’s roll center, its chassis will roll side-to-side more, and that transfer of weight to the outside wheels creates extra grip on that side.Ĭhanges to the lower suspension arm typically have a larger impact than changes to the camber link. In brief, roll center is a way to measure how eager the car is to lean into turns. Pivot height describes the vertical position of the inner, lower suspension arm pins.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
